How to Become a Chief Data Officer (CDO) and Steer Innovation for SMBs, Enterprises, Governments, and More.
Companies are recognizing the immense value of data and its potential to fuel growth and gain a competitive edge. This is where the Chief Data Officer (CDO) position has gained significant importance.
Today, 1 in 4 companies have appointed a CDO, with that number expected to increase in the coming years.
At Bronson Technical Search, we work with SMBs and enterprises across North America to secure high-demand tech talent, like CDOs.
This guide was crafted by our team to help data professionals better understand the role of CDO, what employers are looking for, what the overall job market looks like, as well as a road map to becoming a CDO.
Table of Contents
Introduction to the Role of a Chief Data Officer (CDO)
As the importance of data management continues to rise, Chief Data Officers (CDOs) have emerged as critical players in an organization’s success.
CDOs oversee an organization’s data strategy, ensuring that data is managed effectively, accurately, and in compliance with regulations. Although a relatively new role, the demand for CDOs has surged in recent years, as businesses strive to leverage data to drive growth and innovation.
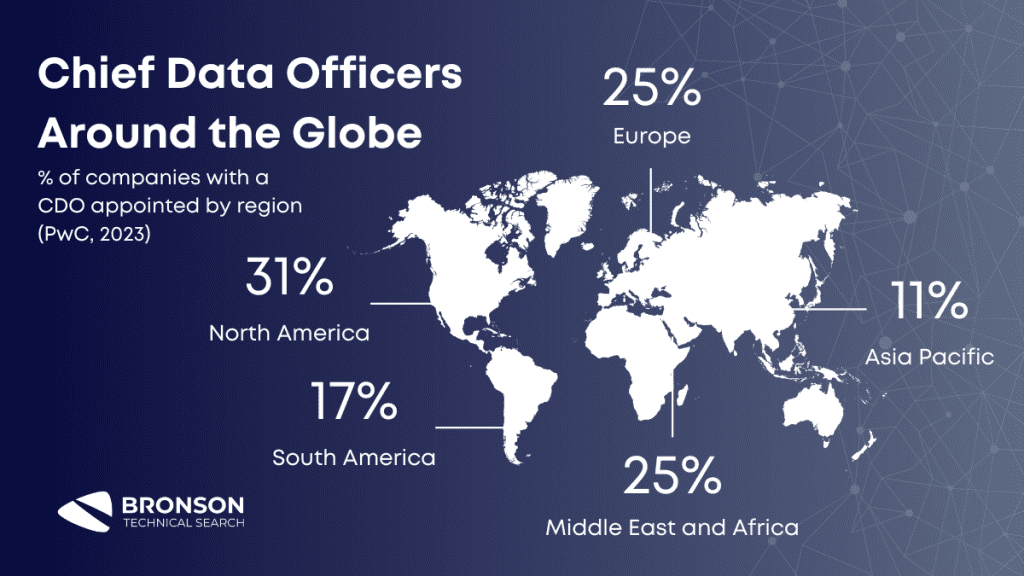
Organizations are increasingly turning to CDOs to better manage, secure, and innovate with their data. According to one study, 27% of the world’s largest publicly listed firms had appointed a CDO as of 2022.
In Europe, where policies like GDPR have made data a top concern, the number is even higher, with 41.6 percent of top organizations having a CDO in place.
What Does a CDO Do?
Chief Data Officers (CDOs) play a critical role in managing an organization’s data strategy. Their responsibilities include developing and implementing policies and procedures for data management, ensuring data accuracy and security, and ensuring compliance with regulations.
As a key member of the executive team, CDOs must work closely with other leaders to ensure that data strategy aligns with overall business goals. Effective communication is also vital for CDOs, who must be able to explain complex data concepts in simple terms and collaborate effectively with other departments to meet the organization’s data needs.
The Importance of a CDO in an Organization
As businesses increasingly rely on data to gain a competitive edge, the role of Chief Data Officer (CDO) has become essential. CDOs are responsible for developing and implementing effective data management strategies that enable organizations to harness the full potential of their data. Their expertise is critical in helping organizations achieve their objectives through data-driven decision-making.
Without a CDO, organizations may encounter significant data management challenges such as inaccuracies, security risks, and non-compliance with regulations. By having a CDO in place, organizations can mitigate these risks and effectively manage their data to drive growth and innovation.
The Skills Required to Become a CDO
Becoming a successful Chief Data Officer (CDO) requires a diverse set of skills and qualities. A strong understanding of data management principles and practices is essential, alongside exceptional analytical and problem-solving skills. Effective communication and leadership are also vital attributes.
CDOs must work closely with other departments and stakeholders to develop and implement data-driven strategies that align with organizational goals. They must be adaptable and responsive to the evolving technological and market trends that influence data management. Successful CDOs are characterized by their ability to collaborate effectively and lead teams to implement innovative solutions.

Tools Used by CDOs
Chief Data Officers (CDOs) work with a variety of tools to manage, analyze, and leverage data effectively.
Here are some common tools CDOs use:
- Data Management and Integration:
- Data warehouses (e.g., Amazon Redshift, Google BigQuery, Snowflake)
- Data integration platforms (e.g., Informatica, Talend, SnapLogic)
- Master data management (MDM) solutions (e.g., IBM InfoSphere, Informatica MDM)
- Data Analytics and Business Intelligence:
- Business intelligence platforms (e.g., Tableau, Power BI, Qlik)
- Data visualization tools (e.g., Tableau, Plotly, D3.js)
- Advanced analytics tools (e.g., SAS, R, Python)
- Data Governance and Compliance:
- Data governance platforms (e.g., Collibra, Informatica Axon, IBM Data Governance)
- Data quality tools (e.g., Talend Data Quality, Informatica Data Quality)
- Compliance management solutions (e.g., OneTrust, TrustArc, RSA Archer)
- Machine Learning and AI:
- Machine learning frameworks (e.g., TensorFlow, PyTorch, scikit-learn)
- Automated machine learning (AutoML) platforms (e.g., DataRobot, H2O.ai, Databricks)
- Natural language processing (NLP) tools (e.g., NLTK, spaCy, Transformers)
- Big Data and Cloud Computing:
- Big data platforms (e.g., Apache Hadoop, Apache Spark, Apache Kafka)
- Cloud computing services (e.g., AWS, Azure, Google Cloud Platform)
- Serverless computing frameworks (e.g., AWS Lambda, Google Cloud Functions, Azure Functions)

Steps to Becoming a CDO
Achieving success as a Chief Data Officer (CDO) requires a combination of education, experience, and skills. Here are some key steps you can take to become a successful CDO:
- Begin by earning a bachelor’s degree in a related field such as computer science, information technology, or business.
- Gain hands-on experience in data management and analysis, which can be gained through internships, entry-level positions, or on-the-job training.
- Pursue a master’s degree in a related field such as data science, business analytics, or information management to deepen your knowledge and expertise.
- Develop leadership experience by taking on management roles or leading data-driven projects within an organization.
- Obtain relevant certifications in data management, data analysis, and leadership to demonstrate your expertise and commitment to the field.
Chief Data Officer Job Responsibilities
While the specific roles and responsibilities of a Chief Data Officer (CDO) can vary depending on the organization, some common responsibilities include:
- Establishing and implementing data management policies and procedures to ensure effective data governance.
- Ensuring data accuracy, completeness, and consistency across all relevant systems and platforms. Managing data security and compliance to protect sensitive information and ensure regulatory compliance.
- Developing and implementing data-driven strategies that align with the organization’s goals and objectives.
- Communicating effectively with stakeholders at all levels of the organization to ensure shared understanding of data-related issues and opportunities.
- Leading data-related projects and initiatives to drive innovation and growth.
- Collaborating with other departments to ensure that data needs are met across the organization.
Challenges Faced by CDOs
While CDOs play a critical role in driving growth and innovation through effective data management, they also face several challenges in their roles.
One of the biggest challenges faced by Chief Data Officers is maintaining compliance with regulations while managing data effectively. This requires a deep understanding of regulatory requirements and the ability to implement data management policies and procedures that align with those requirements. Additionally, CDOs must work collaboratively with other departments to ensure that the organization’s data needs are met.
Another challenge faced by CDOs is staying current with the latest technologies and trends. As new technologies and tools emerge, CDOs must be able to quickly assess their potential impact on the organization’s data strategy and incorporate them into their plans. This requires a commitment to ongoing learning and professional development, as well as a willingness to embrace change and innovation.
Chief Data Officer Salary and Career Prospects
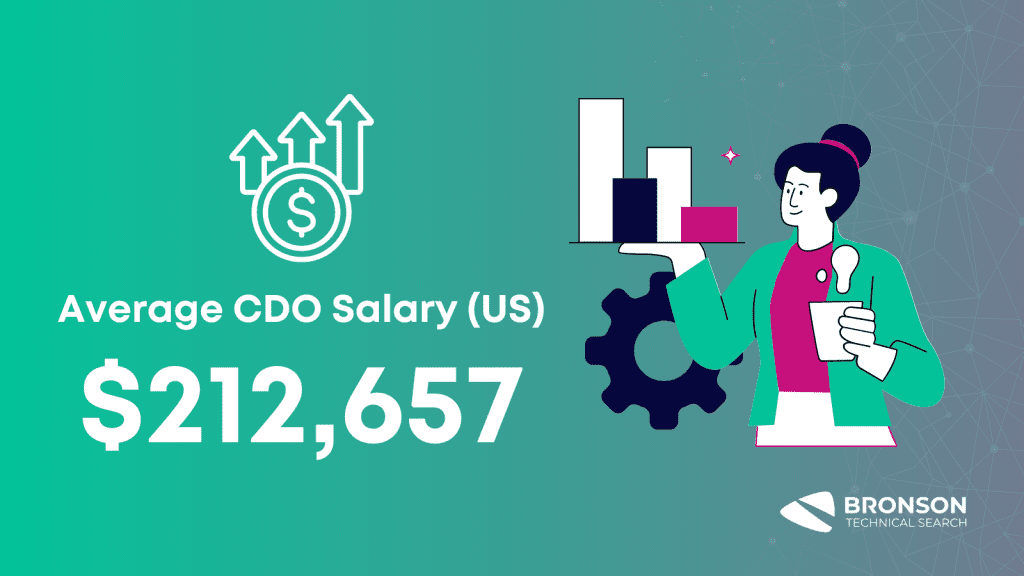
The average salary of a CDO in the United States can vary depending on factors like experience, education, and location. Based on Glassdoor data, CDOs earn an average salary of $212,657 per year.
Looking forward, the demand for CDOs is expected to grow as organizations continue to recognize the value of data in driving innovation and growth.
In 2023, a report by PwC found the number of companies with a CDO appointed have declined compared to 2022. However, adjacent roles have become more common, such as:
- Chief Knowledge Officer
- Chief Analytics Officer
- Chief AI Officer
The role of CDOs is becoming increasingly vital to ensure data is managed effectively to help achieve business objectives.
Courses and Certifications for Aspiring CDOs
For individuals interested in pursuing a career as a CDO, there are various courses and certifications available to enhance their skills and knowledge. Some examples include:
- The gold standard certification for aspiring CDOs is the Certified Data Management Professional (CDMP), which consists of four different levels, run by DAMA International;
- The Data Governance & Stewardship Professional (DGSP) certification offered by the Institute for Certification of Computing Professionals;
- A Master of Science in Data Science offered by several top universities.
These programs can provide a strong foundation in data management principles and practices, as well as develop skills in leadership, analytics, and communication.
Are You Ready to Become a Chief Data Officer?
To become a successful CDO, individuals need to possess a combination of education, experience, and skills.
The role of a CDO is crucial in ensuring effective data management that drives growth and innovation in organizations. Following the steps outlined in this guide, such as obtaining relevant education and experience, can help individuals prepare for a successful career as a CDO.
As the field of data management continues to evolve, CDOs must stay updated with the latest technologies and trends. By continuously learning and adapting, individuals can remain well-positioned for long-term success in this exciting and dynamic field.
A final (but important) note: Based on my years of experience as a technical recruiter with Bronson Technical Search, I can confirm that no two paths to becoming a CDO are the same. We always look at a candidate’s unique experiences and qualities they bring to the table.
If you have any questions about becoming a CDO, or you are looking to hire one for your organization, feel free to reach out to me at [email protected]

By Colin Kieran, Managing Partner, Bronson Technical Search
FAQS – How to Become a Chief Data Officer (CDO)
Chief Data Officers often encounter challenges such as cultural resistance to data-driven decision-making, data silos, legacy systems, regulatory compliance, and talent acquisition and retention. Overcoming these challenges requires strong leadership, effective communication, and a strategic approach to data management and analytics initiatives.
Data governance is crucial for a Chief Data Officer as it ensures that data is managed, protected, and utilized in a consistent and compliant manner across the organization. Establishing robust data governance frameworks helps mitigate risks, maintain data quality, and enhance trust in the organization’s data assets.
Successful Chief Data Officers possess a diverse skill set that includes strong leadership, strategic thinking, communication, and collaboration abilities. Additionally, they should have deep expertise in data management, analytics, technology, and business acumen to effectively drive data-driven decision-making across the organization.
Becoming a Chief Data Officer typically requires a combination of education, experience, and specific skills. Many CDOs have advanced degrees in fields such as computer science, data science, or business administration. They also often have extensive experience in data management, analytics, and leadership roles within organizations.
A Chief Data Officer (CDO) is responsible for managing and leveraging an organization’s data assets to drive business growth, innovation, and efficiency. They oversee data strategy, governance, quality, and analytics initiatives to ensure that data is effectively utilized to support organizational goals and objectives.
While both roles are critical for leveraging technology and data to support organizational goals, they focus on different aspects of information management.
A Chief Data Officer (CDO) primarily oversees the management, governance, and utilization of data assets to drive business value, ensure data quality, and promote data-driven decision-making.
On the other hand, a Chief Information Officer (CIO) is responsible for the overall technology strategy and infrastructure of the organization, including hardware, software, networks, and cybersecurity.
While the CDO focuses on maximizing the value of data, the CIO is more concerned with the broader IT landscape and ensuring that technology aligns with the organization’s strategic objectives.
Organizations can benefit from having a Chief Data Officer by gaining valuable insights from their data assets, improving decision-making processes, enhancing operational efficiency, mitigating risks, identifying new business opportunities, and driving innovation and competitive advantage in the marketplace.



